Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis (Rats and Mice)

Psoriasis is the most prevalent immune-mediated skin disease in adults, and affects approximately 25 million people in North American and Europe alone1. Psoriasis is a complex, multifactorial disease and the exact mechanism of psoriasis is not yet fully understood1,2. In the past, most psoriasis research was performed in a xenotransplant model, where skin from a psoriasis patient is grafted onto immunodeficient mice. Although this model is useful, these experiments are laborious, expensive, and require considerable expertise and technical skill3,4. The development of the imiquimod-induced model of psoriasis is a simple, acute, cheap model that has been used with increasing frequency to better understand the inflammatory process leading to psoriasis, as well as a high-throughput screening of potential therapeutic agents3,5.
Induction:
Starting on Study Day 0 and continuing daily for the duration of the study, 75mg (mice) or 150mg (rats) of 5% imiquimod cream is applied to the shaved skin on the back.
Disease Parameters/Progression:
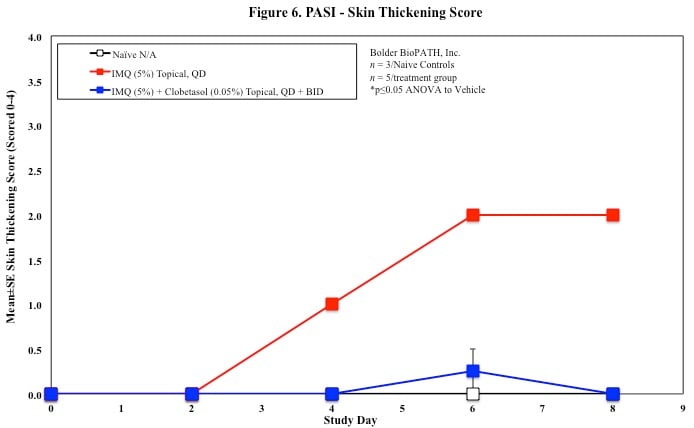
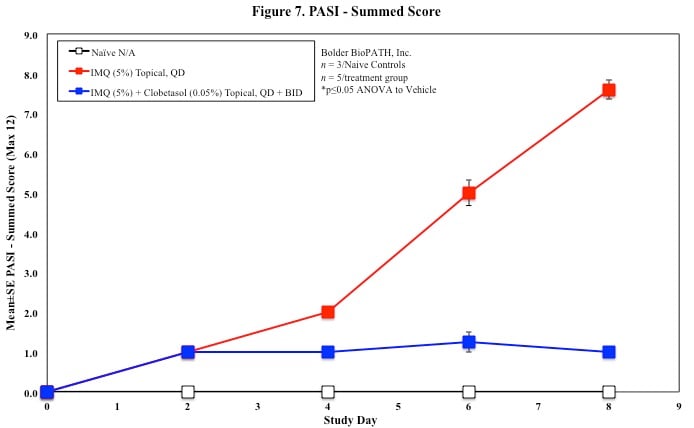
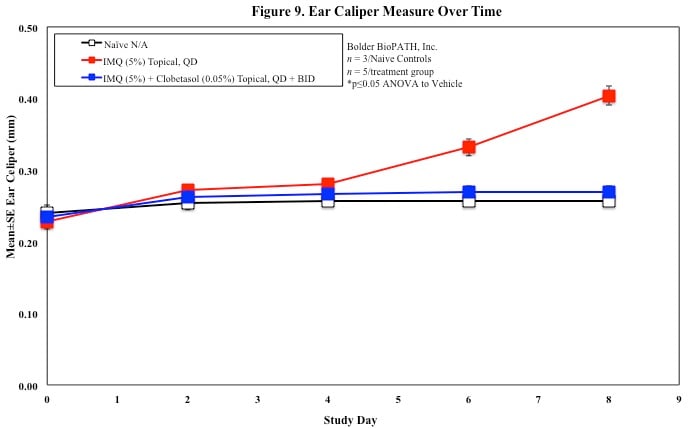
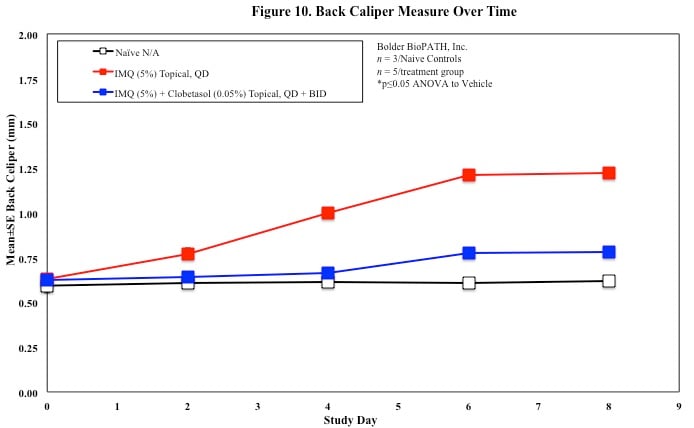
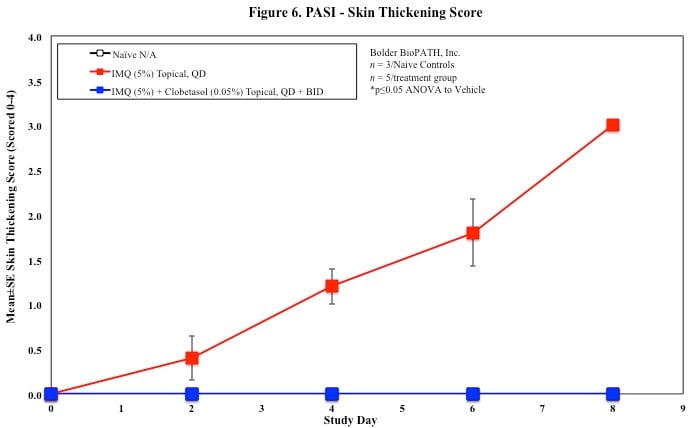
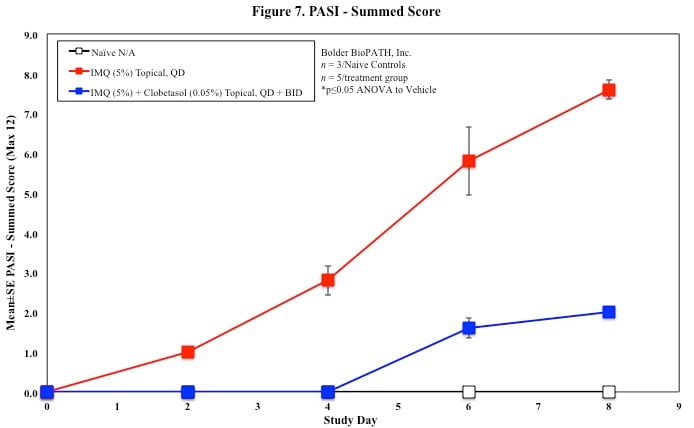
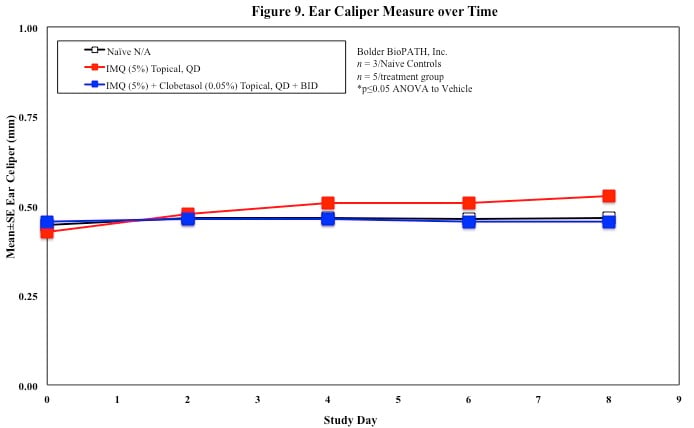
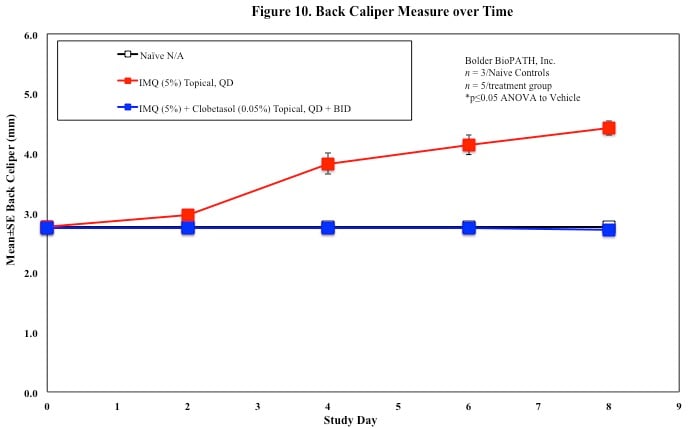
In mice, redness and scaling significantly increase by Study Day 6; whereas visual thickening score and caliper measurements increase at day 4.
Dosing Paradigms:
- Prophylactic (Developing) – Dose prior to daily IMQ.
- Established (Therapeutic) – Dose after IMQ.
- Route of administration: Topical, SC, PO, IP, IV
Clinical Assessment:
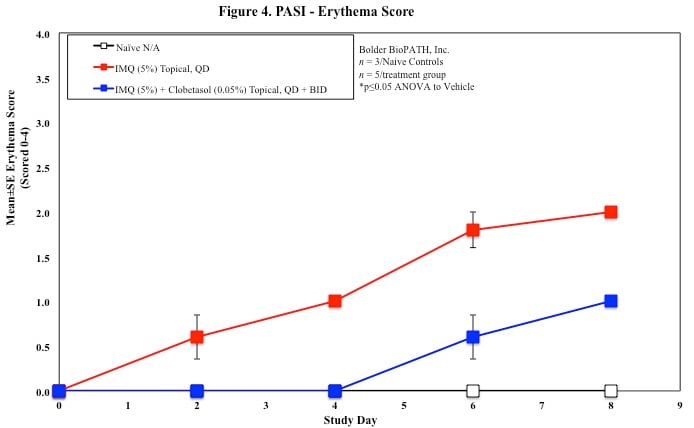
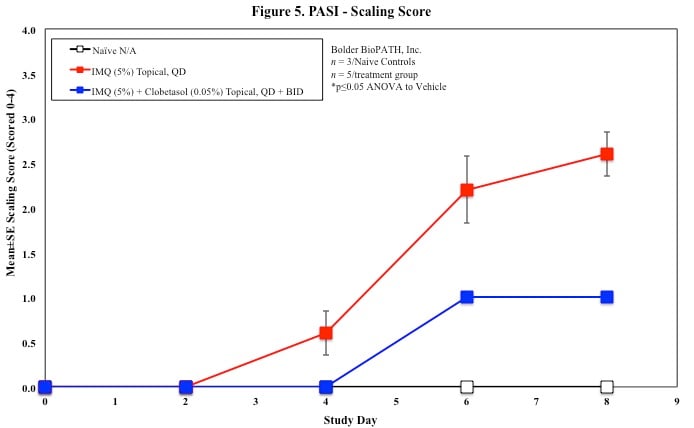
PASI Scoring
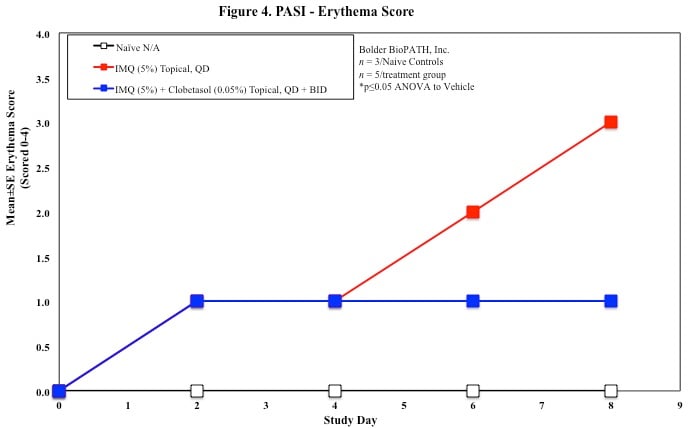
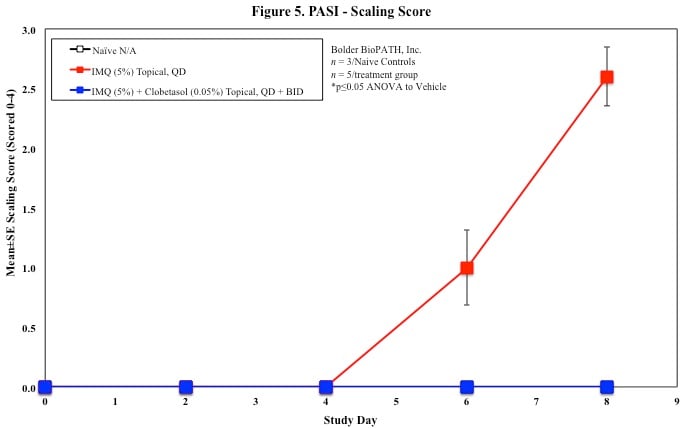
Every other day animals are scored for erythema, scaling, and skin thickening as follows:
- 0 = None
- 1 = Slight
- 2 = Moderate
- 3 = Marked
- 4 = Very Marked
Skin caliper measurements are also taken every other day using a Digitrix II micrometer. Biopsy punches of the skin may also be taken and weighed.
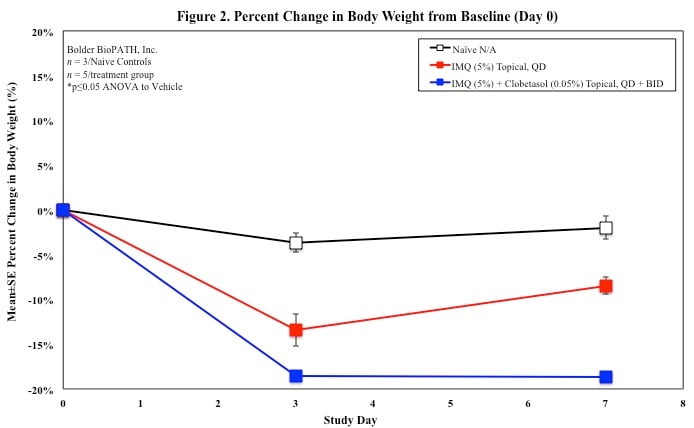
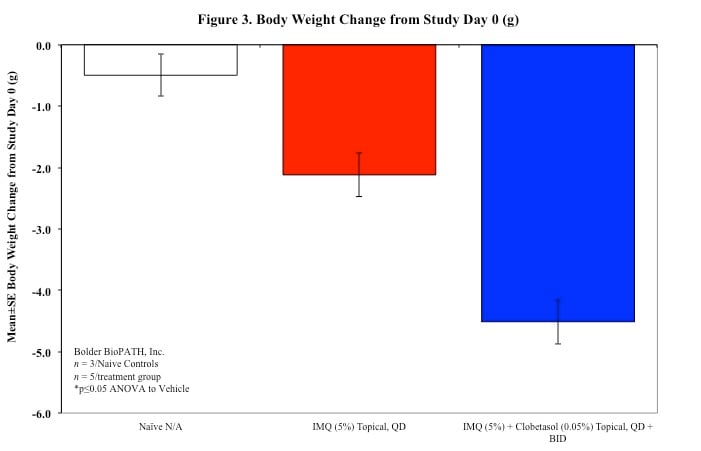
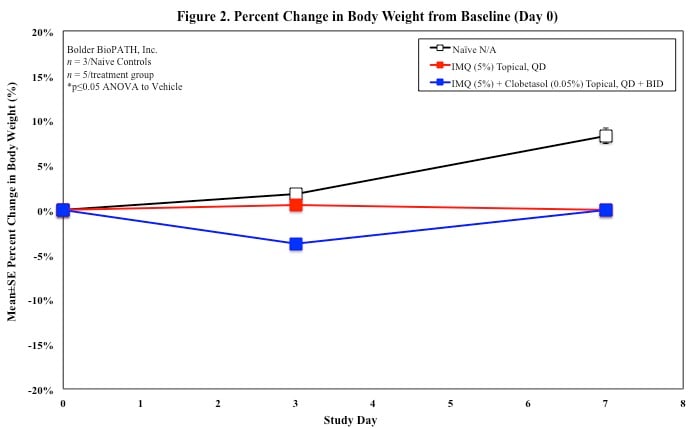
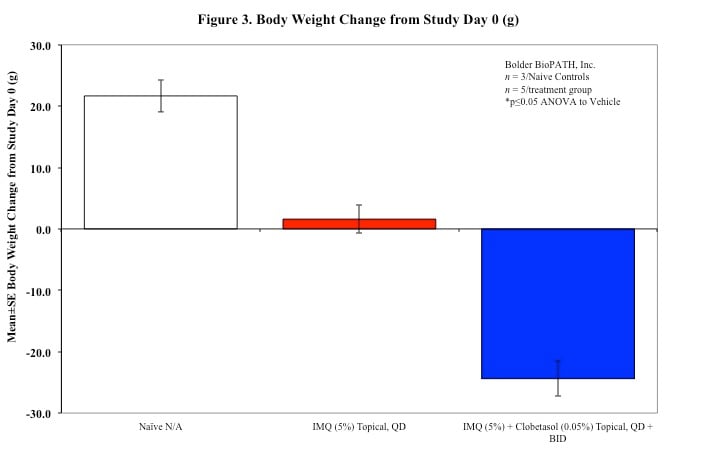
Sample Data (Click on image to enlarge):
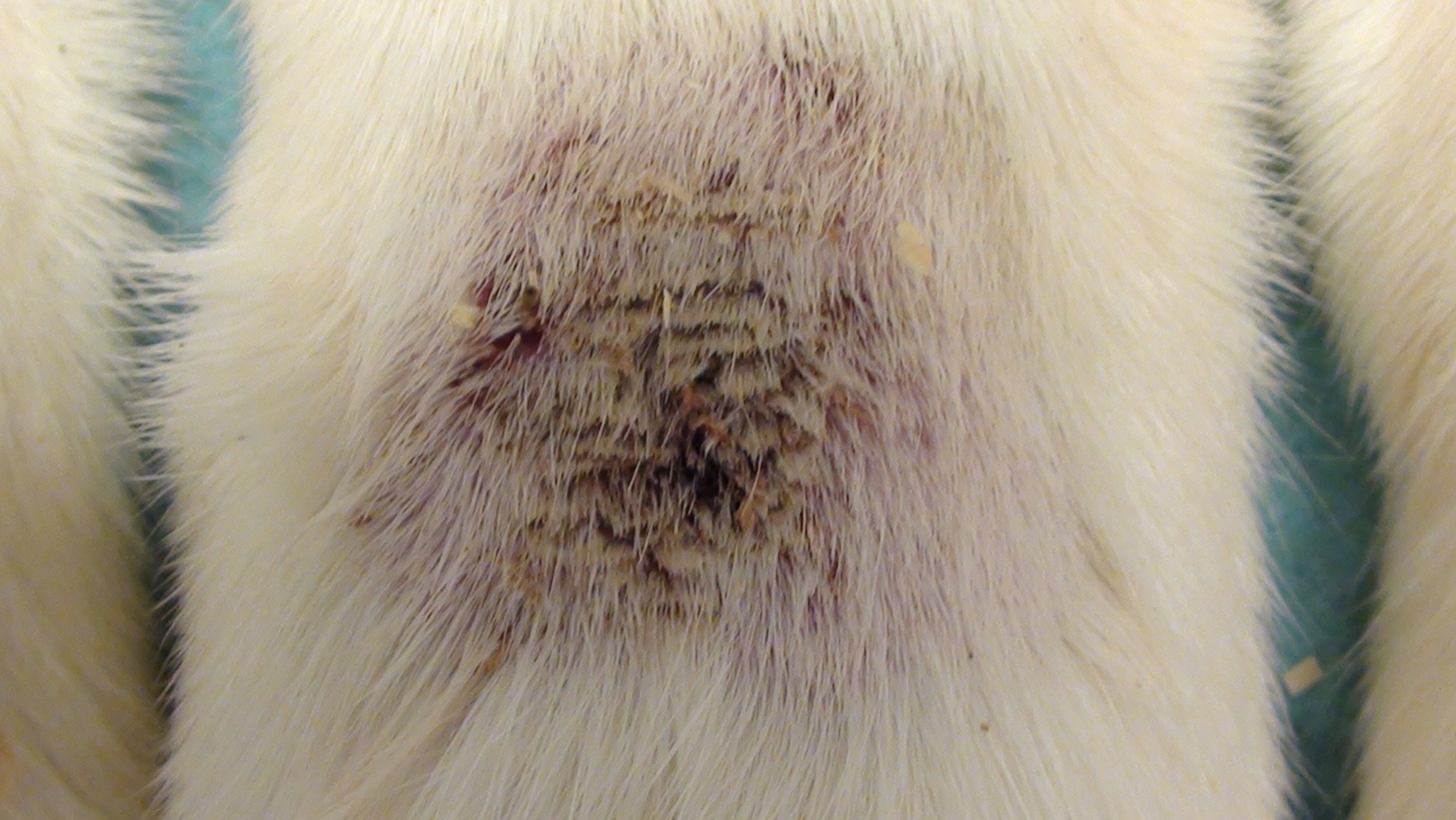
Mouse Clinical
Mouse Photographs
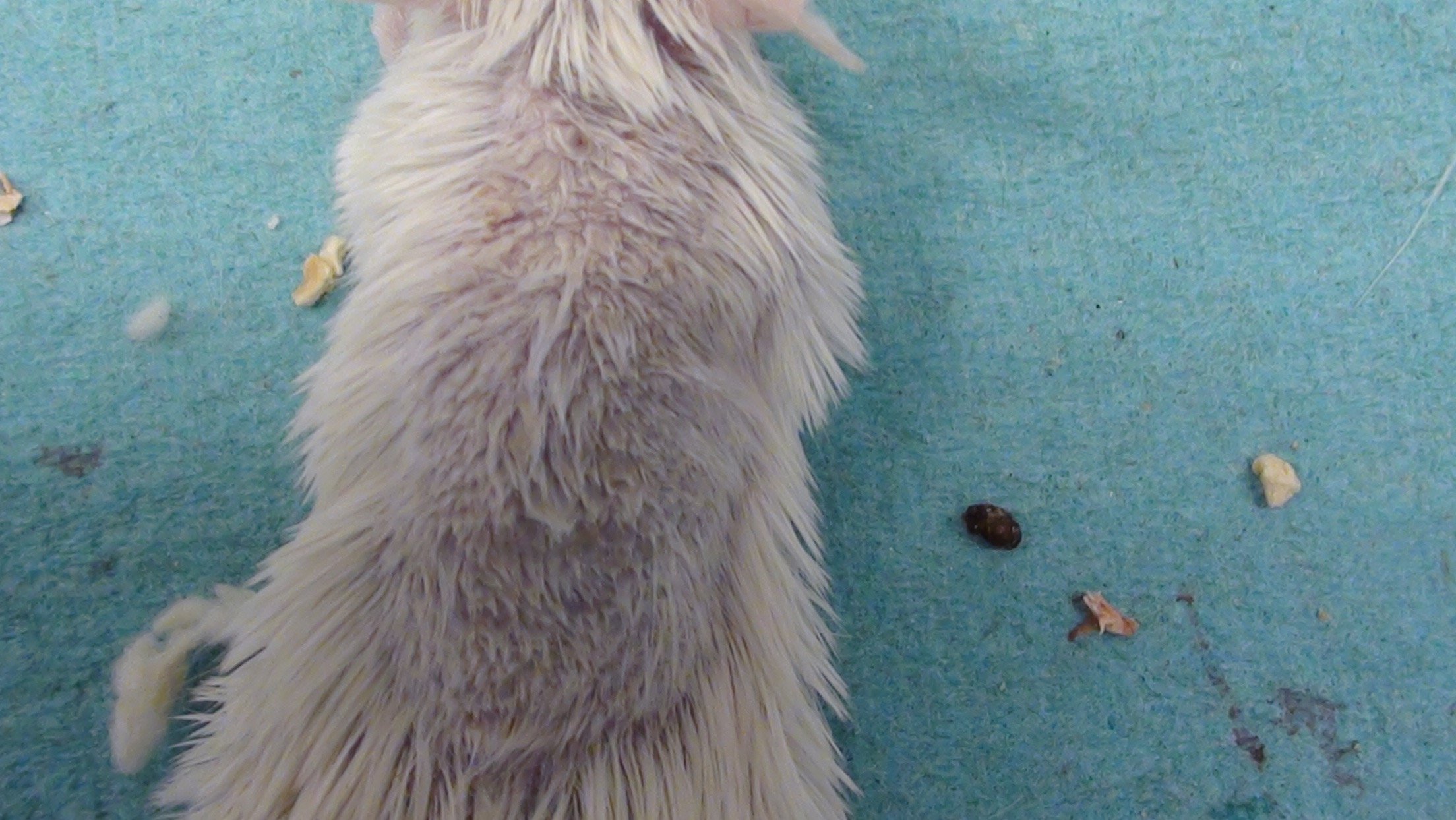
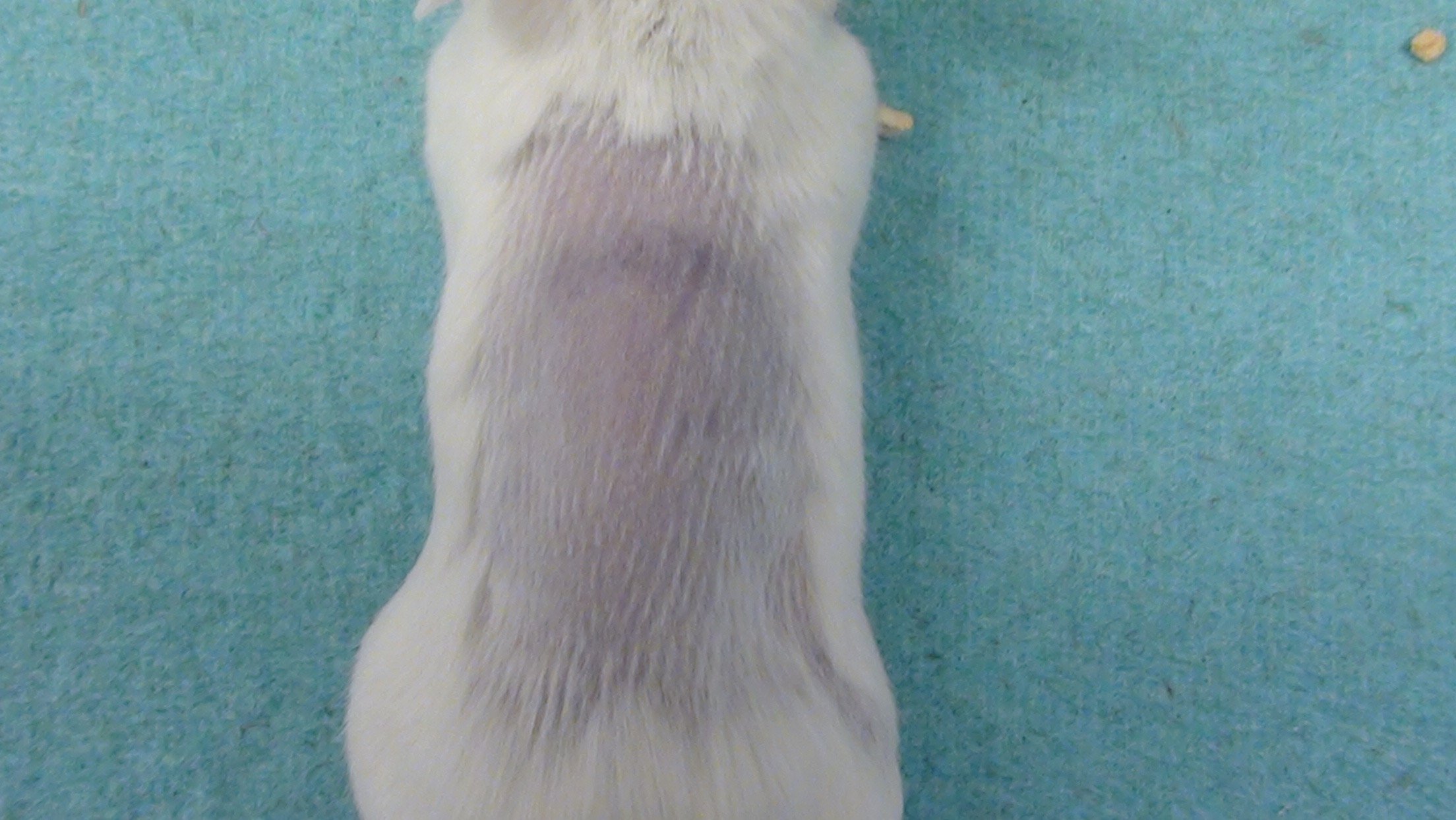

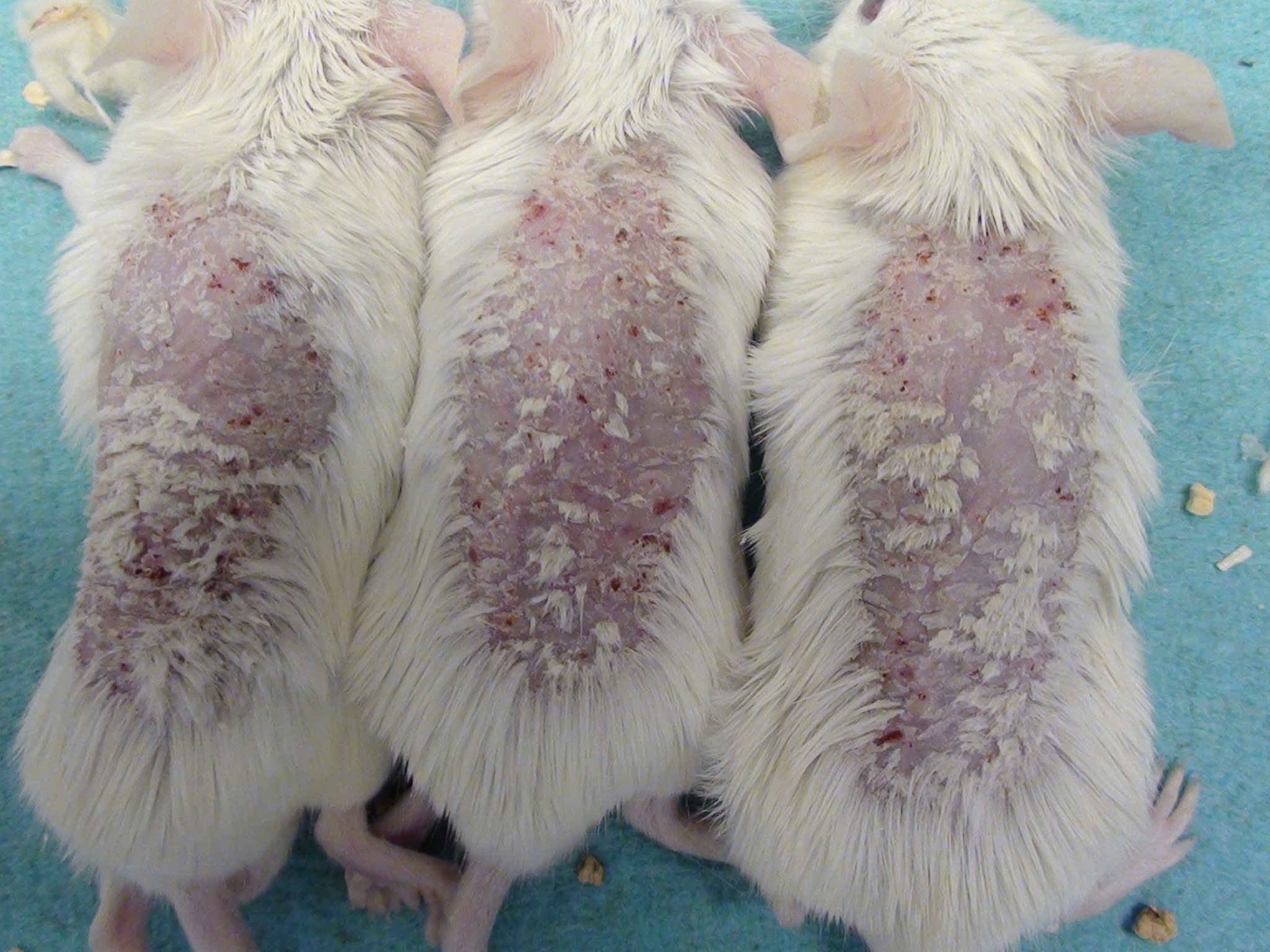
Rat Clinical
Rat Photographs
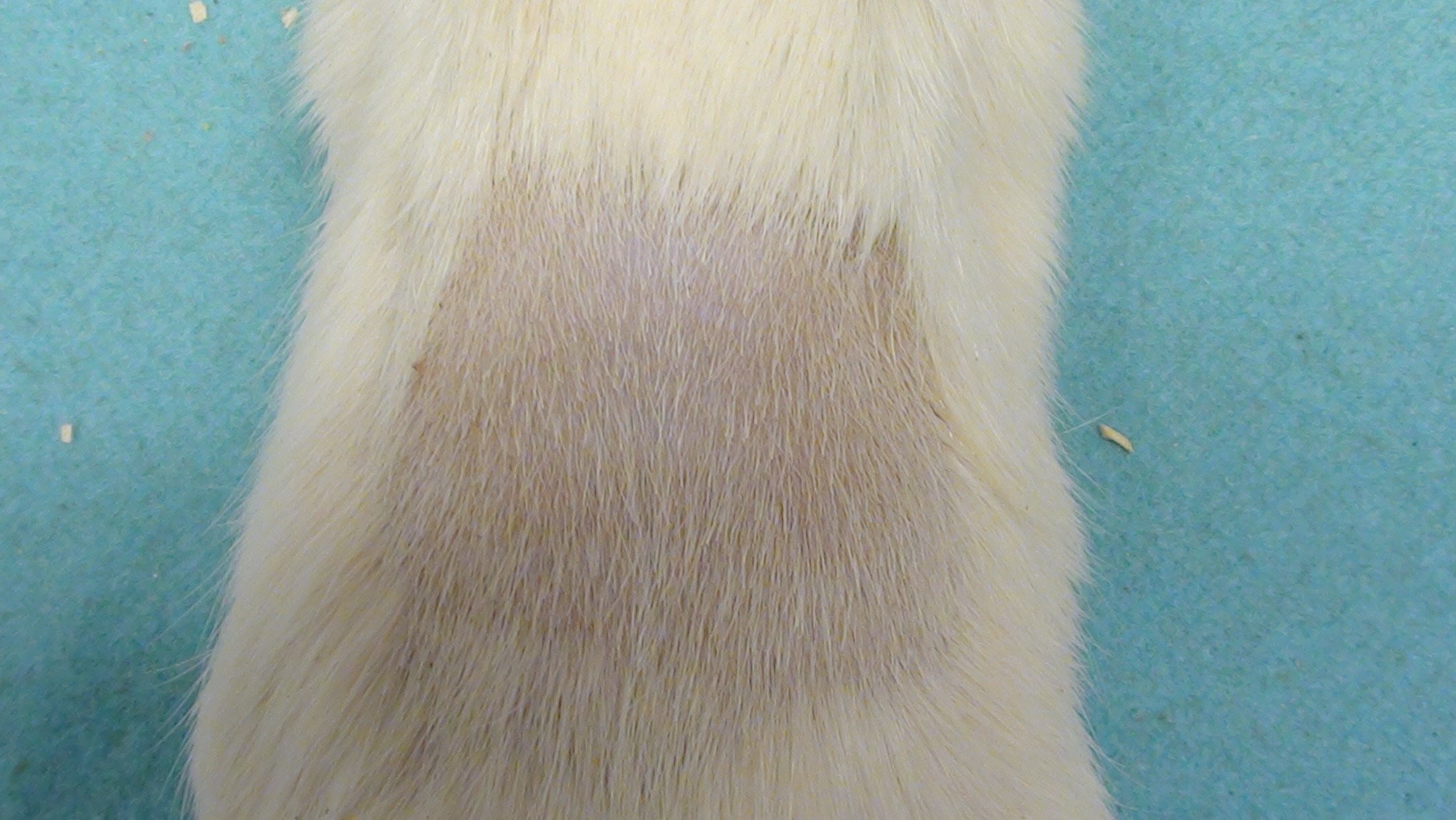
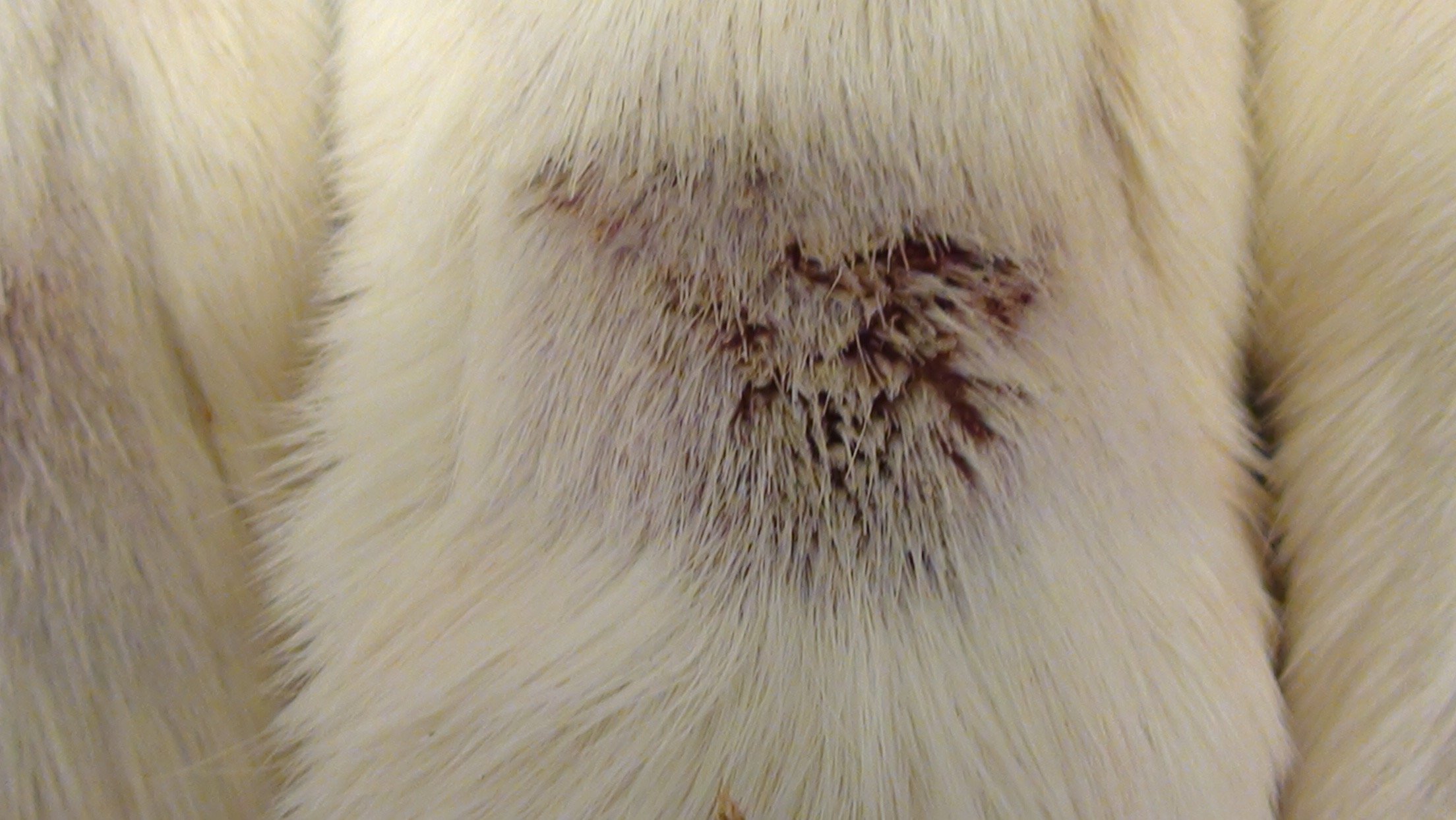
Notes:
The imiquimod-induced model of psoriasis is a simple model that has been used with increasing frequency to better understand the inflammatory process leading to psoriasis, as well as a high-throughput screening of potential therapeutic agents.
Optional Endpoint
- PK/PD blood collections
- Cytokine/chemokine analysis via Luminex(R)
- Other sandwich ELISAs
- CBC/clinical chemistry analysis
- Histopathologic analysis
- Immunohistochemistry analysis
References
- Sun J, Zhao Y, and Hu J. Curcumin inhibits imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like inflammation by inhibiting IL-1beta and IL-6 production in mice. PLoS ONE. 2013; 8(6):e67078.
- Pantelyushin S, et al. Rorγt+ innate lymphocytes and γδ T cells initiate psoriasisiform plaque formation in mice. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2012; 122(6):2252-2256.
- Flutter, B and Nestle FO. TLRs to cytokines: mechanistic insights from imiquimod mouse model of psoriasis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013; 43:3138-3146.
- Van der Fits L, et al. Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 Axis. J-Immunol. 2009; 182:5836-5845.
- Swindell WR, et al. Genome-wide expression profiling of five mouse models identifies similarities and differences with human psoriasis. PLoS ONE. 2011; 6(4):e18266.
For more information about IMQ-Induced Psoriasis (Mice and Rats), contact us here.
Related Pages
General Inflammation
- Oxazolone Induced Ear Delayed Type Hypersensitivity (Mouse)
- mBSA Induced Footpad Delayed Type Hypersensitivity (Mouse)
- Carrageenan Induced Paw Edema (Rat & Mouse)
- Lipopolysaccharide Induced Cytokine Cascade (Rat, Mouse)
- IL-23 induced Psoriasis (Mouse)
- IMQ induced Psoriasis (Rat, Mouse)
- Monosodium Urate-Induced Gout
- Zymosan Induced Peritonitis
- Non-Lethal Cerulein-Induced Pancreatitis (Rat, Mouse)